Autism
- Home
- Autism
What is Autism?
Autism is also called as ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder- Autism is just one condition. It is a range of symptoms commonly grouped into ASD). Autism is a neuro-developmental disorder, abnormalities in neural circuits and development. The symptoms appear early in life. Autism is a disorder of communication (social impairment) and interaction with others, restricted interests and repetitive behaviors causing difficulty in learning and function. The complaints vary in a wide range in type and severity. Autism (ASD) affects a person’s ability to learn, interact and reason in several ways. The common symptoms include:
Communication
- Avoiding eye contact, not looking at people when talking
- Not responding when called by name
- Difficulty in conversation
- Unconnected facial expressions and gestures
Repetitive and restricted behavior
- Repeating certain behaviors, words, phrases (like flapping their hands, fidgeting their fingers, rocking, spinning, making sounds)
- Difficulty with changes in routine, things
- Special interests in certain topics and objects ( door handles, locks)
- Extreme or less sensitivity to sense of light, touch and sound
Every autistic person is unique. The symptoms can be categorized as:
- Sensory sensitivity -Over-responsive
- Sensory seeking
- Difficulty with changes
- Poor motor coordination
- Emotional and behavioral challenges
- Communication deficits
- Intellectual and learning
The symptoms may be excess of what need not be or deficit of what need be.
Autism and intellectual ability: Some autistic may have high IQ and some average and some low IQ. 38%- 67 % of autistic children have varying degree of intellectual disability (ID). 24% of autistic children are in the borderline of IQ (71%-85%). ID is more in females.
What are the Autism Spectrum Disorders?
- Asperger’s syndrome
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD)
- Rett Syndrome
Asperger’s syndrome
Some of the world’s most successful personalities were diagnosed as ASD ( Asperger’s) or qualified to be called autistic by applying the criteria of ASD.
- Albert Einstein- Scientist
- Charles Darwin- Biologist
- Bobby Fischer- Chess Grandmaster
- Bill gates- Microsoft founder
- Michaelangelo- painter
- Isaac Newton-Physicist
- Elon Musk- Entrepreneur
- Nikola Tesla-Inventor
- Leonardo da Vinci- artist
- Alfred Hitchcock- Director
- Steven Spielberg- Director
The list includes Vincent van Gogh, Thomas Alwa Edison, Alexander Graham Bell, Henry Ford, Beethoven, Mozart and manymore including Nobel prize winners….
- It is also called high functioning autism. They have intense passion for a certain topic only. They had limited and narrow range of interests and accomplished great things. Many of them were diagnosed as such or their strengths were remarkable focus and persistence, aptitude for recognizing patterns and attention to detail. In common, they all had, difficulty with social interactions, restricted interests, and desire for sameness.
Symptoms of Asperger’s syndrome
- Poor eye contact
- Miss social cues
- Speak in a flat tone
- Fail to read the body language and facial expressions
- Trouble in responding to conversation
- Repeat words, phrases
- Hate change and follow the routine schedule, habits
- Interest in any one topic or subject
- Show few emotions.
Most common symptom in autism is intolerance or hypersensitivity to external stimuli like touch, sound or light which is a result of impaired electrical circuits within the brain caused by inflammation. They have difficulty in shifting from one stimulus to other. There is a failure to prune unnecessary connections with development. There is also an excessive activation of inflammation in the brain.
Autism peaks in early childhood. Early identification signs may be any of the following and one should remember that all the symptoms need not manifest. The list serves as an early screener:
- Avoids eye contact
- No response when called by name by nine months
- No display of joy, sad, angry, or surprise facial expressions by nine months
- Doesn’t engage in interactive games by 12 months
- Makes no gestures at 12 months
- Does not share interests with others by 15 months (i.e.,not showing an object that he/she likes)
- Does not point to show you something interesting by 18 months
- Does not recognize when others are harmed or unhappy at 24 months
- Does not observe or engage in play with other children by 36 months
- Does not pretend to be someone else during play by 4 years
- Does not perform for you in song, dance, or acting when five years old
- Sets toys or other items in a line and becomes irritable if the order is changed
- Easily upset by the slightest changes
- Repeatedly uses the same words or phrases
- Uses the same playstyle with toys every time
- Focuses concentration on object or components (like switches, wheels, moving parts)
- Possesses obsessive interests
- Must adhere to specified procedures
- Flapping hands, rocking the body, or circling oneself
- Demonstrates unique reactions to sounds, smells, tastes, sights, or feelings
- Delayed language and motor skills
- Delayed abilities in learning or thinking
- Inattentive, impulsive, or hyperactive behavior
- Seizure or epilepsy disorder
- Unusual sleeping/eating patterns
- Digestive disorders
- Unusual emotions or mood swings
- Anxiety, tension or the absence of fear, or unexpectedly high levels of fear
Autism Diagnosis
Autism screening is done when the child is 9,18,24 and 30 months of age. Currently, the diagnosis of Autism relies on behavioral evaluation. The diagnostic feature is either developmental or behavioral. Routine investigations like blood test, MRI/CT scans are unlikely to contribute to the diagnosis of autism. Diagnosis is made best by the mother by observing the behavior. There are several rating scales employed for the diagnosis of autism. Earlier the diagnosis is done, the better is the treatment outcome.
- Aberrant Behavior Checklist (ABC)
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale ( CARS)
- Autism Spectrum Rating Scale (ASRS)
- Ages and Stages Questionnaire ( ASQ)
- Screening Tool for Autism in Toddlers and young Children (STAT)
- Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT)
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)
- Social responsiveness Scale ( (SRS)
- Repetitive Behavior Scale ( RBS)
- Some special scales are:
- Autism Spectrum quotient
- Rivvo autism Asperger Diagnostic scale
Autism is a disorder of brain functioning, more specifically the connectivity within the brain. The connectivity is a process. It is inter- neuronal connectivity or functioning between different areas and between both hemispheres. This electrical activity in the brain can be recorded as conventional Electro Encephalo Graph. Conventional EEG reveals a general picture of brain’s functioning, Quantitative EEG Brain map reveals all that is happening in terms of inter neuronal communication, their connectivity and strength. Autism being a connectivity disorder, QEEG Brain map is an ideal source to identify and locate the defective or malfunctioning. A properly recorded QEEG Brain map points out the defects in detail that aids in the treatment. QEEG Brainmap helps in locating the type and site of malfunction. The defect may either be the speed or the link or the power of electrical activity in the brain. QEEG Brainmap is descriptive of what is happening in the brain. EEG shows reduction in gamma activity.
What causes autism?
Autism is caused by several associated factors rather than a single factor. The condition surfaces when these multiple factors collude together. In a genetically predisposed individual, the environment plays a major role in making the condition manifest. The earliest environmental factor linked to autism is depriving the infant of mother’s touch and skin to skin warmth, wherein lots of communication takes place between mother and infant, immediately after birth. First few hours after birth, upto 12-24 hours, is more critical to avoid development of autism. Neo-natal isolation and stressful early life cause autistic like behaviors including social deficits, repetitive behaviors, anxiety-depressive like behaviors.
Co- existing conditions:
ADHD and autism may co-exist frequently. Rarely seizure disorder is seen co-existing with Autism. Anxiety, depression and gastro intestinal problems co- exist with autism. Autistic children with GI problems had different gut flora than the others. Sensory processing Disorder may coexist with autism.
How is the brain affected in autism?
Autism is mainly a disorder of brain’s internal connectivity. Brain cells are affected at some point during development either before or during or after birth. The connectivity problem is found to be responsible for many of the major symptoms seen in autism leading to inability to shift from one stimulus to other or hypersensitivity to sound , light or touch. There is also failure to prune unwanted synapses and scavenge the broken down cells. This leads to continual activation resulting in inflammatory reaction of the brain and release of cytokines, an inflammatory marker. The inflammation correlates with communication and behavior issues.
Autism Treatment
Autism is not a behavioural disorder but a neuro- developmental disorder. The treatment aims to correct or restore the impaired brain functions of altered connectivity and inflammation. Autism treatment aims to improve the overall functioning and behaviour. Earlier it is started, the better it is. Early identification of the condition is crucial for a good outcome.
In a condition like autism, which is is a general problem of electrical connectivity, worrying about a specific behaviour is unrewarding. The treatment aim shall be holistic, as the brain gains greater control, the unwanted behaviors go away.
Autism treatment falls under two categories: 1. Non interventional and 2. Interventional.
Non-interventional vs Interventional
- Targets symptoms Cause oriented
- Not precise Focused and precise
- Indefinite course Specified period
- Passive Actively restores the error in connectivity Backed by research studies Cost effective
- Interventional: This method includes Trans-cranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
- Non-interventional: Interventional methods are well researched and are under various stages of advancement.
1. TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
TMS improves functional connectivity within and between brain regions, neuroplasticity, brain functions. Effects are not limited to the stimulated regions alone but also noted in other functionally interconnected areas.
TMS is non-invasive magnetic stimulation of the brain and it improves social interaction and decreases anxiety-depressive like behaviours. Also aids in neuroplasticity, a form of rewiring the brain.
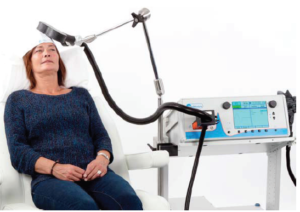
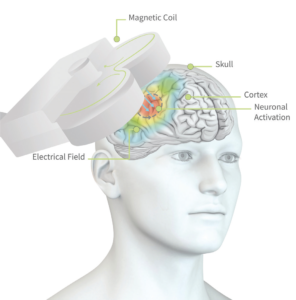
A small coil positioned in specific spots over the scalp identified by the psychiatrist , produces rapidly changing magnetic field that passes through scalp and skull bone. This magnetic activity influences brain’s activity. The coil placement site, the type, speed, number and strength of the magnetic pulse is determined by various protocols as determined by the psychiatrist, depending on the requirement. The treatment duration may range from 8 minutes to 40 minutes. Total number of sessions vary from 15-30 that is spaced out over a period. The sessions extend over 4- 6 weeks. Safety as the first priority has been proven in all the studies.
What are the conditions rTMS is used:
rTMS is used for the following conditions :
Drug resistant depression Social and general anxiety Autism
ADHD PTSD OCD
Schizophrenia Fibromyalgia Chronic pains
Sleep disturbances Stroke recovery Migraine
Alcoholism Post stroke aphasia Addictions
Smoking Eating disorders Panic disorder
Treatment session: During the session, the magnetic coil will be placed over the selected site. A test pulse will be given to determine the individual’s sensitivity ( resting motor threshold), based on which the treatment pulse strength will be decided and the session started. During session, a clicking or tapping sound will be heard and a feeling of tapping will be felt. This may be felt over the forehead or over eyes and face. The magnetic pulse will be on and off during the entire session at the chosen speed. These sessions are always customised.
Safety: The safety of TMS is well established even in the presence of other neuropsychiatric conditions like epilepsy, ADHD etc. If scalp pain or discomfort appears, it vanishes immediately after the session without any interference.

Advantages of TMS treatment:
- High success rate in symptom reduction for autism
- Improvement in social behaviour and speech
- It is non-invasive.
- It is non- sedative.
- It is free from side effects.
What do we expect by TMS treatment?
- Decreases the repetitive behaviour and actions
- Irritability and depression are controlled
- Enhances motor performance
- Brings under control of attention deficits
When do we see the results of TMS treatment?
The noticeable change in behaviour begins after 5-10 session and is slow and steadily progressive. Occasionally, the changes may not manifest for a longer period.
Types of TMS
Various modes and protocols are followed and the number of pulses, speed, strength, type of coil, duration of treatment vary with different modes. They include:
- Repetitive TMS with Figure of 8 coil HF and LF methods
- Theta burst in shortest duration
- Deep TMS with H coils for deeper penetration.
2. Hyper Baric oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
HBOT is another promising alternate treatment for autism. HBOT targets brain inflammation and damage. HBOT improves speech, communication, social skills and overall behaviour. In autism, there is reduced blood flow to critical regions in the brain connected with executive functions and emotions. Reduced blood flow impedes neuroplasticity ( brain rewiring).
HBOT delivers high concentrations of oxygen at increased atmospheric pressure levels. This improves inflammation, blood flow to starved areas and boosts immunity and reduces inflammation.
HBOT corrects mitochondrial dysfunction ( powerhouse of the nerve cells) and reduces oxidative stress and increases antioxidant production thus protecting against oxidative stress.
Hyper Baric Oxygen Therapy improves behaviour, memory, language, verbalisations, cognitive functions, eye contact, repetitive behaviour, motor skills, gastro intestinal complications which is common in autism due to change in gut flora.
HBOT is a safe procedure and free from adverse side effects.
Non interventional: This method includes
- Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Cognitive behaviour therapy.
- Neurofeedback
- Medications
Of all these, medications and Neurofeedback are semi interventional.
Medications: Select medicines approved by FDA are used to control irritability and behavioural symptoms like aggressive behavior and self- harm.
Neurofeedback is a Biofeedback method of training the brain. Neurofeedback aims to correct the connectivity disorder and power of the brain waves. All these methods target a specific cause to restore normalcy in behaviour.
More popular speech therapy and Occupational therapy are effective only in borderline cases. Active intervention is required when the severity is moderate or severe.
What is the outcome of the condition or the treatment?
An autistic may be a life- long condition, needing an on-going support, depending on the severity. An autistic may live a normal life with right support. Early intervention is the key factor in achieving the goal. The goal shall be one of long term learning to gradually shape behaviour. About 15-25% of autistic children recover fully and live a normal meaningful life with intervention and appropriate support.
The diagnosis of autism is not the end of everything. Every autistic has his/her own strengths and abilities to succeed.


