Introduction
Hello there! I’m Dr. Murugappan, and I run a Clinic right here in Chennai, focused on offering top-notch medical services, including understanding the profound effects of alcohol on the brain. Whether you’re a casual drinker or someone who’s concerned about your alcohol consumption, it’s crucial to know how alcohol impacts your brain. Let’s dive into this topic and shed some light on what really happens in our heads when we drink.
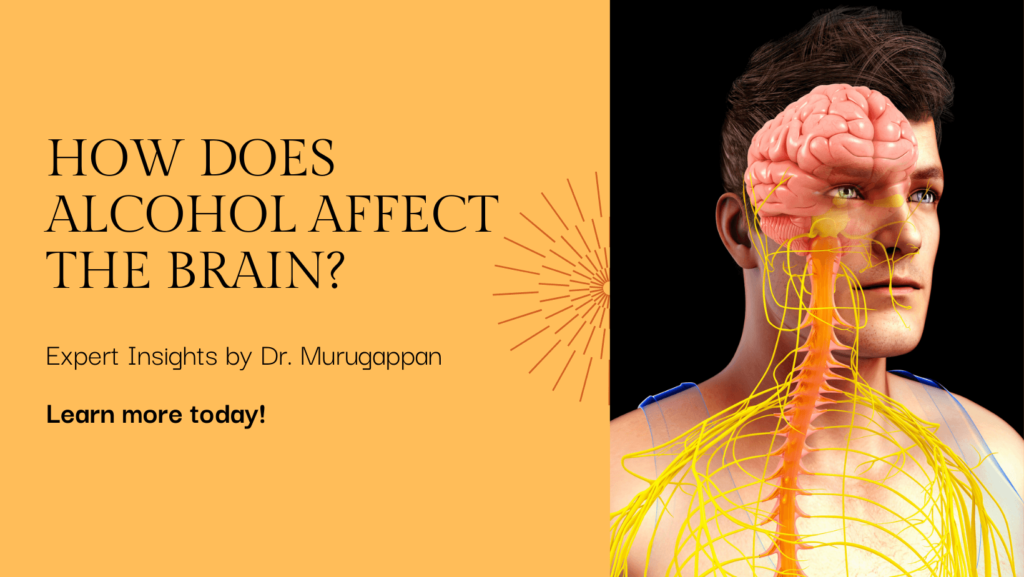
What Happens When You Drink Alcohol?
When you take that first sip of alcohol, it might seem harmless, even relaxing. But have you ever wondered what’s going on in your brain? Initially, alcohol makes you feel more sociable and less anxious, thanks to its depressive effects on the central nervous system. But this is just the tip of the iceberg.
The Chemistry of Alcohol in the Brain
Alcohol affects the brain’s chemistry almost immediately. It interacts with neurotransmitters, the chemicals that transmit signals in your brain. Alcohol primarily targets GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which has a calming effect, and glutamate, which has the opposite effect, exciting the brain. The result? A slowed down, relaxed feeling, but also impaired cognitive functions.
Short-term Effects of Alcohol on the Brain
So, what happens in the short term? Here’s a quick rundown:
- Cognitive Impairments: Your ability to think clearly takes a hit.
- Behavioral Changes: You might become more talkative, or even aggressive.
- Mood Swings: Alcohol can make you euphoric one moment and tearful the next.
- Poor Decision-making: Ever done something you regretted after drinking? That’s alcohol impairing your judgment.
Long-term Effects of Alcohol on the Brain
Now, let’s talk long-term. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to:
- Brain Damage: This includes a reduction in brain size and brain cell loss.
- Cognitive Decline: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and a decrease in problem-solving skills.
- Mental Health Disorders: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Alcohol and Neurotransmitters
To understand this better, let’s dig deeper into neurotransmitters:
- GABA and Glutamate: Alcohol increases GABA’s calming effects and decreases glutamate’s excitatory effects. This dual action is what makes you feel relaxed and less inhibited.
- Dopamine and Serotonin: Alcohol boosts dopamine, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, which contributes to its addictive nature, and affects serotonin, impacting mood regulation.
Alcohol-Induced Brain Disorders
Some serious disorders can arise from heavy drinking:
- Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome: A severe condition caused by a deficiency in vitamin B1 (thiamine), leading to brain damage.
- Alcohol-Related Dementia: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to symptoms resembling Alzheimer’s disease.
Risk Factors for Brain Damage Due to Alcohol
Not everyone who drinks will experience severe brain damage, but certain factors increase the risk:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of alcoholism can make you more susceptible.
- Drinking Patterns: The amount and frequency of alcohol consumption play a significant role.
Effects of Alcohol on Young Brains
Young adults, listen up! Your brains are still developing, and alcohol can disrupt this process, leading to long-term consequences such as:
- Impaired Brain Development: Affecting memory and learning capabilities.
- Behavioral Problems: Increased risk of engaging in risky behaviors.
Gender Differences in Alcohol’s Effect on the Brain
Did you know alcohol affects men and women differently? Here’s how:
- Men vs. Women: Women generally feel the effects of alcohol more quickly than men due to body composition and hormonal differences.
- Hormonal Influences: Women’s hormonal cycles can affect how alcohol is metabolized, potentially leading to more severe effects.
Alcohol and Brain Recovery
Is there hope for recovery? Absolutely! The brain has an incredible ability to heal itself if you:
- Stop Drinking: The sooner you quit, the better your chances of recovery.
- Seek Medical Help: Therapies and medical treatments can significantly aid in recovery.
Preventive Measures and Healthy Habits
Prevention is better than cure, so here are some tips:
- Moderation: Limit your alcohol intake.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Stay Informed: Knowledge is power – understanding the risks can help you make better choices.
Treatment Options for Alcohol Dependence
If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol dependence, there are effective treatments available:
- Detoxification Programs: Medical supervision to safely manage withdrawal symptoms.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Long-term support to maintain sobriety.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps in changing the thought patterns that lead to drinking.
Patient Testimonials and Success Stories
At our Clinic, we’ve seen numerous success stories. For instance, Raj, a 45-year-old engineer, turned his life around with our help. After struggling with alcohol dependence for years, he is now sober and leads a fulfilling life. Stories like Raj’s are a testament to the power of determination and the right support.

Conclusion
Understanding how alcohol affects the brain is crucial for making informed choices about drinking. It’s not just about the immediate effects but the long-term impact on your cognitive health. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol, don’t hesitate to seek help. Our Ultimate Brain Clinic in Chennai is here to provide the support and treatment needed for a healthier, alcohol-free life.
FAQs
Can the brain recover from alcohol damage?
Yes, the brain can recover from alcohol damage, especially if drinking is stopped early and appropriate medical treatment is sought.
How long does it take for alcohol to affect the brain?
Alcohol can start affecting the brain within minutes of consumption, with more noticeable effects after just a few drinks.
Is occasional drinking harmful to the brain?
Moderate, occasional drinking is generally not harmful for most people, but heavy or binge drinking can lead to significant brain damage over time.
What are the early signs of alcohol-related brain damage?
Early signs include memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, and impaired judgment.
How can one reduce the risk of brain damage from alcohol?
Reducing the risk involves moderating alcohol intake, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and seeking medical advice if you suspect a problem.
Make an Appointment Today and Shine Brighter!
Call us at(+91)9444437698!
For more information on Depression, visit Ultimate Brain: Depression.
Watch on YouTube.
Contact us on WhatsApp.
Connect with her on LinkedIn.
For additional wellness services, check out Silkee.

